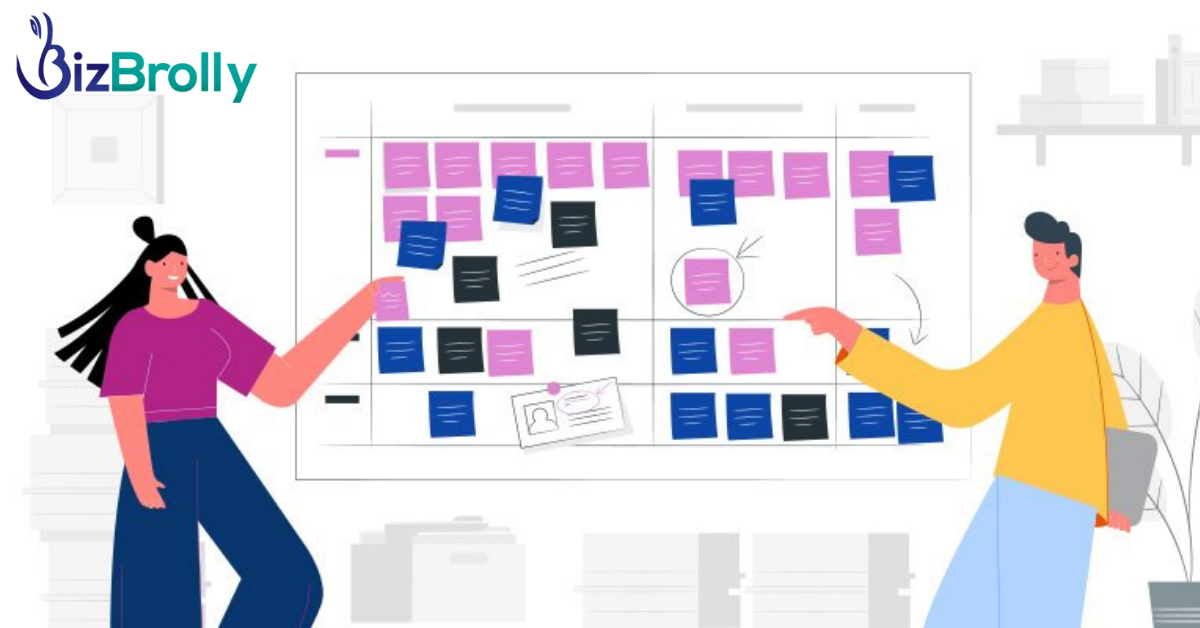
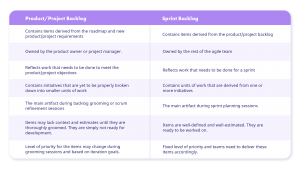
A product backlog records and focuses on the errand level subtleties needed to execute the essential arrangement set out in the roadmap. The backlog ought to convey what’s next in the improvement group’s plan for the day as they execute on the roadmap’s 10,000-foot view vision. Normal things in a product backlog incorporate client stories, bug fixes, and different errands.
The Product Backlog in a scrum is an interpretation of how your group will convey the vision that is laid out on an agile roadmap. In numerous ways, it is a goliath to the daily agenda for your development group..
The Sprint Backlog is an arrangement by and for the Developers. It is a profoundly apparent, ongoing status of the work that the Developers intend to achieve during the Sprint to accomplish the Sprint Goal. Subsequently, the Sprint Backlog is refreshed all through the Sprint as more is learned. It ought to have sufficient detail that they can examine their advancement in the Daily Scrum.
Product backlog vs sprint backlog
Journey of a Product Backlog
You always start a product ideation process with a vision to build a structure of everything happening around the product. Vision is always followed by a detailed plan to mark the checkpoints and processes related to it, which is followed by a product roadmap. A product roadmap is like a summary that maps the vision and direction of the product.
In the end, there is a need for a product backlog to prioritize the event and checkpoint. The prioritization processes are influenced by various factors that help to achieve the overall development of the product..
How to prioritize product backlog items?
RICE
RICE represents Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort. When estimating Reach, groups hope to evaluate the number of clients who will utilize the element benefit from the Backlog thing. Sooner rather than later, this number should come from real information, not a supposition or prediction. Sway requests that the group make a reasonable deduction regarding what probable the element in the Backlog will mean for a singular client. Certainty estimates the group’s trust in their assessments. Exertion estimates how much work and time the group should give to the Backlog thing to finish it.
Pros of RICE
Puts clients in the middle.
Depends on information and sold measurements
Extensive
Cons of RICE
Tedious.
Math-oriented.
Information driven, without a ton of information groups may need to make many predictions..
Opportunity scoring depends on two diagrams to rank the Backlog things. To start with, they utilize a fulfillment diagram, positioning how clients like a component. Then, at that point, they utilize a significance chart, estimating how much clients esteem a component. In inspecting the two graphs’ groups recognize what baffles their clients and what their clients need..
Pros of Opportunity Scoring
Centers around ROI (Return on Investment).
Works for various sorts of Backlog
Helps observe holes between client need and value gave.
Cons of Opportunity Scoring
Groups need to have a current product, doesn’t work for new elements.
Limited in scope.
Japanese scientist Noriaki Kano made the Kano model during the 1980s. The Kano model estimates client fulfillment to focus on the Backlog. Utilizing Kano, the group scores Backlog things by a few rules: Must-be, appealing, one-layered, detached, and switch. Important highlights are those that clients need for the product to work. Clients consider one-layered elements to be significant and attractive. Alluring elements add worth and fulfillment to the cause. Uninterested elements have little or no worth to clients..
Pros of Kano
Positions are highlighted by their worth.
Client-focused.
Gives simple knowledge into qualities and shortcomings of a component.
Cons of Kano
Kano doesn’t detail asset necessities.
Agile groups use Moscow since Moscow is straightforward and simple to utilize. The abbreviation represents Must, ought to, could, and would. Moscow permits groups to decide the general significance of Backlog things. Must mean any Backlog thing needed for a product to work. Should represent things that have high worth to the client. Could Backlog things are little fixes and highlights. Would things have the most reduced significance and can be added to a future Backlog in the event that the group doesn’t have time..
Pros of Moscow
Simple to utilize.
Not very specialized or numerical.
Quick
Cons of Moscow
Zoomed-in view, not an outline.
Not sequenced.
Product Backlog Templates.
Here are is certain product backlog examples that help in making better product backlog with the processes.
