The Role of Business Intelligence in Agile Software Development


Did you know that executives don’t receive the data they need 65% of the time when making critical business decisions? This alarming gap in agile business intelligence highlights why organizations struggle to maintain competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced market.
When we examine business intelligence analytics more closely, the challenges become even more apparent. According to a Gartner survey, 90% of corporate strategies will explicitly mention information as a critical enterprise asset and analytics as an essential competency in 2023. Despite this recognition, 50% of data remains inconsistent, and 20% contains errors, significantly hampering the effectiveness of business intelligence services.
Agile business intelligence offers a solution by using agile software development methodology for BI projects to reduce time-to-value and quickly adapt to changing business needs. Unlike traditional approaches, agile business process for intelligence operates on an iterative principle, providing new features to end users sooner than waterfall processes. Furthermore, it enables faster and more accurate decisions through data-driven decision-making.
In this article, we’ll explore how agile BI methodology transforms business intelligence workflow through just-in-time planning and incremental delivery. We’ll examine its role in software development, how it integrates with existing agile frameworks, and the significant benefits it brings to business intelligence project management.

Image Source: SlideTeam
“Agile is an attitude, not a technique with boundaries.” — Alistair Cockburn, Co-author of the Agile Manifesto, software development expert
Agile Business Intelligence (ABI) has emerged as a powerful approach for delivering data insights that adapt quickly to the ever-changing needs of software development teams. Let me walk you through what makes this methodology so valuable for today’s software projects.Definition of Agile BI and its core principles
Agile Business Intelligence refers to the application of agile software development methodology specifically for business intelligence projects. At its core, ABI is a systematic approach that delivers BI solutions through iterative development cycles, continuous collaboration, and adaptive planning.
The fundamental principles that define Agile BI include:
Essentially, ABI operates on an iterative principle, providing new features to end users sooner than traditional waterfall processes, which typically deliver only the final product at the end of the project. This technique allows the requirements and design phases to overlap with development, thus reducing development cycles and achieving quicker delivery.
Traditional business intelligence follows a linear, sequential approach that often begins with extensive pre-planning and building each infrastructure layer one at a time. This means a significant upfront investment in complex backend systems for the IT environment and data warehousing, with user-facing systems coming later in the project.
In contrast, Agile BI focuses on:
Additionally, Agile BI emphasizes metrics-based progress tracking, regular performance evaluation, and data-informed prioritization, making it particularly suitable for dynamic software development environments.
In today’s rapid business environment, the decision window is continuously shrinking – business answers are needed not in months or weeks, but right now. This reality makes Agile BI particularly valuable for several reasons:
First, Agile BI enables fast feedback loops and delivers products that better meet client needs. By implementing BI solutions using agile methodology, IT teams can deliver higher quality solutions to the organization.
Second, the approach dramatically improves user adoption. In an Agile development environment, IT and business personnel work together, often in the same room, refining business needs in each iteration. This collaboration increases end-user engagement by emphasizing the changing needs of non-technical business users.
Third, organizations achieve increased return on investment with shorter development cycles by minimizing IT resources and time while delivering relevant reports to end-users. The iterative approach also reduces risk, as problems can be identified and addressed early in the development process.
Finally, concerning data quality, traditional approaches often struggle with inaccurate data () and inconsistent information (50% rate). Agile methodology addresses this by motivating the auto-discovery of new data sources and automated upgrade of metadata repositories to accommodate new information.20% error rate
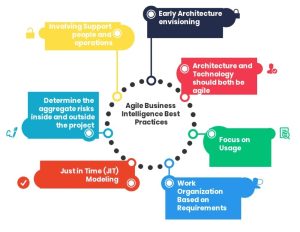
Image Source: PAT Research
The integration of business intelligence into agile methodologies represents a paradigm shift in how development teams approach data-driven decision making. Unlike traditional approaches where analysis often happens after development, agile BI creates a symbiotic relationship between data insights and software delivery.
Data-driven sprints transform how teams prioritize and execute work. Instead of relying solely on intuition, teams leverage analytics to make informed decisions about sprint goals and resource allocation. This approach helps identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and ultimately boost productivity throughout the development cycle.
At the core of this integration lies the concept of iterative feedback loops—cyclical processes where teams regularly gather, analyze, and act on data to continuously improve. These loops consist of four essential components:
The empirical process of moving from an initial idea through implementation and analysis forms the basis for iteration, with completion of this process marking the end of an iteration rather than a predetermined timeframe. Consequently, each iteration can be viewed as validating or rejecting a specific lean hypothesis.
In Scrum, BI enhances key events by providing metrics that inform sprint planning, daily stand-ups, reviews, and retrospectives. For instance, velocity tracking helps teams forecast future sprint capacities, moreover, burndown charts visualize progress throughout a sprint.
Kanban, with its focus on making work visible, pairs naturally with business intelligence dashboards. BI tools help enforce work-in-progress (WIP) limits by highlighting bottlenecks and supporting continuous flow optimization.
Data Driven Scrum (DDS), specifically designed for data science teams, integrates BI at its foundation. Unlike traditional Scrum’s fixed-length sprints, DDS employs capability-based iterations that allow for logical chunks of work to be released coherently. This flexibility proves particularly valuable in BI environments where task estimation can be unreliable.
Sprint planning benefits from BI through enhanced backlog prioritization. Teams use data insights to estimate the value, effort, and probability of success for each backlog item, enabling more effective planning sessions.
Daily stand-ups become more effective when supplemented with real-time analytics dashboards. Instead of merely reporting status, team members can reference concrete metrics to discuss progress and identify impediments.
Sprint reviews gain depth through BI-powered demonstrations that showcase not just completed functionality but actual performance metrics and user adoption data, fostering more productive conversations about completed work.
Retrospectives benefit from analysis of sprint data to identify trends and patterns, creating a culture of ongoing refinement based on quantitative insights rather than just subjective impressions.
“Don’t just get better once; get better constantly. Always be looking for something to improve.” — Jeff Sutherland, Co-creator of Scrum, Agile thought leader
Implementing agile business intelligence delivers numerous concrete advantages for development teams seeking to enhance their performance metrics and product quality. Organizations that leverage this approach gain tangible benefits in multiple operational dimensions.Real-time reporting for faster decision-making
Real-time data analysis fundamentally transforms how development teams operate. Companies with agile BI capabilities can make confident decisions quickly, reducing uncertainty and delays associated with traditional data analysis methods. Indeed, this approach allows businesses to:
As a result, teams gain the ability to identify problematic areas faster, either through analysis or by avoiding unfortunate sudden consequences. This speed is especially crucial since the decision window in today’s business environment continues to shrink—answers are needed not in months or weeks, but immediately.
One of the most powerful advantages of agile BI comes from enhanced partnership between business and IT organizations. Subsequently, this collaboration creates a co-ownership mentality, with both parties sharing responsibility for success and failure.
Practically speaking, effective collaboration often involves matrixing IT business intelligence competency center (BICC) developers to specific business areas. These developers remain anchored in IT standards while embedding themselves within business units to understand what information matters most. This arrangement ensures enterprise reports remain “certified” while still allowing individuals across the organization to freely explore data.
Agile BI accelerates value delivery through its iterative, incremental approach. Obviously, this contrasts with traditional methods that might spend months or years developing solutions before releasing them.
Development teams using agile BI deliver smaller, frequent improvements that provide business value sooner. Forthwith, this translates to higher stakeholder engagement since users gain value before project completion. For example, Tradeware improved cash flow throughout the year by optimizing stock levels in small increments, guided by BI insights.
Similarly, agile BI elevates risk management through predictive analytics capabilities. By leveraging historical sprint metrics, machine learning models, and time-series forecasting techniques, teams can identify emerging risks related to delivery slippage, quality degradation, or capacity constraints.
Throughout development cycles, real-time dashboards enable continuous monitoring of key performance indicators such as sprint velocity, burndown rates, and team throughput. This approach helps with early risk identification in business operations, processes, and markets. Notably, organizations using predictive analytics for risk management can achieve in predicting project outcomes.85% accuracy, 82% precision, and 85% recall
Despite the immense value agile business intelligence offers, many organizations encounter obstacles during implementation. Understanding these challenges first helps teams prepare for a smoother transition to data-driven agile processes.
Organizations frequently struggle with data trapped in disconnected pockets across departments, systems, or platforms. These silos emerge from various factors including legacy systems, function-specific software solutions, inconsistent data definitions, and restrictive security practices. Hence, maintaining multiple isolated systems increases costs through separate support teams, redundant software licenses, and inefficient maintenance efforts.
Integration complexity presents another formidable barrier. As application platforms multiply, traditional integration technologies struggle to handle the influx. Hard-coded, custom-built integrations require significant technical skill yet remain cumbersome to support when requirements change.
Misalignment among stakeholders creates significant friction that undermines product success. Without clear priorities, teams face situations where “when everything is important, nothing is important”. This challenge often manifests as:
Traditional BI tools frequently struggle with the speed requirements of agile environments. Legacy systems designed for stable, batch-oriented applications create technical debt as organizations maintain outdated systems because replacing them requires substantial effort.
Overcoming these challenges requires multi-faceted approaches. Cross-functional teams with varied expertise help break down silos through collaboration. Meanwhile, cloud-based BI tools eliminate overlapping legacy systems by utilizing SQL-based modeling layers that are more agile, collaborative, and flexible.
Ultimately, effective strategies include establishing clearly defined data ownership and governance, implementing data validation processes, and investing in modern Integration Platform-as-a-Service (iPaaS) solutions that enable seamless integration between on-premise systems and cloud applications.
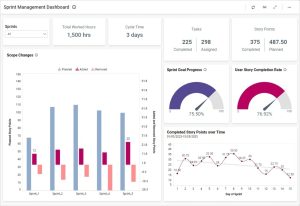
Image Source: Bold BI
In practice, agile business intelligence shines through practical applications that deliver measurable value to development teams. Let’s examine how BI tools function in real-world software environments.
Sprint velocity dashboards offer teams critical insights into their performance patterns. These visualizations display both planned and completed story points, enabling accurate forecasting of future sprint capacities. Teams leveraging velocity charts can track historical data to determine average completion rates, helping teams plan more effectively. Burndown charts, alongside velocity metrics, monitor how well a team executes against their sprint plan. Upon examination of these metrics, management can identify trends that inform resource allocation decisions throughout development cycles.
Embedded analytics transforms how teams track feature usage within applications. Project managers utilize these insights to monitor key performance indicators including completed story points by sprint, tasks completed, and team performance. Throughout development, embedded analytics helps track product release metrics, component usage, and incident rates. This visibility allows teams to identify improvement areas and fix operational weaknesses before starting new projects.
Within DevOps environments, BI tools track crucial deployment metrics that determine development success. DORA metrics—deployment frequency, lead time for changes, time to restore service, and change failure rate—provide standardized measurement frameworks. High-performing teams achieve and 182× lower change failure rates. Real-time monitoring dashboards deliver instant visibility into application health, allowing teams to create custom views displaying their most critical metrics.127× faster lead times
Agile Business Intelligence has emerged as a cornerstone for modern software development teams seeking competitive advantage through data-driven decisions. Throughout this article, we explored how BI transforms agile processes by providing critical insights at every development stage. The integration of business intelligence with agile methodologies creates a powerful synergy that addresses the alarming for executive decision-making.65% gap in data availability
The stark contrast between traditional and agile BI approaches highlights why teams increasingly adopt the latter. While traditional methods often deliver results after months or years, agile BI provides immediate value through iterative development cycles. Additionally, the collaborative nature of agile BI breaks down silos between business and IT departments, fostering shared ownership and responsibility.
Real-time reporting stands out as perhaps the most significant advantage of agile BI implementation. Teams can identify issues faster, respond to market changes immediately, and make confident decisions without unnecessary delays. Similarly, the incremental delivery approach ensures stakeholders receive value throughout the project lifecycle rather than waiting for final completion.
Despite these benefits, organizations still face significant challenges when implementing agile BI. Data silos, integration complexity, stakeholder misalignment, and tooling limitations can hinder adoption efforts. However, these obstacles can be overcome through cross-functional teams, cloud-based BI tools, and clearly defined data governance frameworks.
Real-world applications demonstrate the practical value of agile BI in software development. Sprint velocity dashboards help teams accurately forecast capacities, embedded analytics track feature adoption, and DevOps metrics monitor deployment success. These applications provide tangible evidence of how BI enhances agile processes.
Ultimately, agile Business Intelligence represents much more than a technical implementation—it embodies a fundamental shift in how development teams approach data. Organizations that successfully integrate BI with agile methodologies position themselves for greater adaptability, faster innovation, and more responsive customer solutions. The future of software development undoubtedly belongs to teams that can harness the power of data through agile business intelligence while continuously adapting to evolving market demands.
Q1. What is Agile Business Intelligence and how does it differ from traditional BI? Agile Business Intelligence applies agile software development principles to BI projects, focusing on iterative development, continuous collaboration, and adaptive planning. Unlike traditional BI, which often takes months or years to show results, Agile BI delivers small, usable increments quickly, involves users throughout the process, and adapts readily to changing business needs.
Q2. How does Agile BI integrate with existing agile frameworks in software development? Agile BI enhances agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban by providing data-driven insights for sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives. It supports metrics-based progress tracking, informs backlog prioritization, and enables real-time performance monitoring through BI dashboards, aligning seamlessly with agile ceremonies and practices.
Q3. What are the key benefits of implementing Agile BI in development teams? Implementing Agile BI offers several benefits, including faster decision-making through real-time reporting, improved collaboration between business and IT departments, quicker product delivery through incremental insights, and enhanced risk management using predictive analytics. These advantages lead to more responsive and efficient development processes.
Q4. What challenges might teams face when implementing Agile BI, and how can they be overcome? Common challenges include data silos, integration complexity, lack of stakeholder alignment, and tooling limitations. These can be addressed by forming cross-functional teams, adopting cloud-based BI tools, establishing clear data governance, and investing in modern integration solutions. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for successful Agile BI implementation.
Q5. How is Agile BI used in real-world software development scenarios? In practice, Agile BI is used to track sprint velocity through dashboards, monitor feature adoption with embedded analytics, and measure DevOps deployment metrics. These applications provide teams with valuable insights for forecasting, resource allocation, and continuous improvement throughout the development lifecycle.

In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly advanced, with neural ...
Explore more
In the modern manufacturing landscape, Machine Learning (ML) is emerging as a ga...
Explore more


D-23, Sector 63, Noida,
UP - 201307
141 Westgate Dr, Edison,
NJ - 08820

4 Black lion court, Mill road, Kent, UK – ME71HL

2207, 2220 Lakeshore Blvd W, Toronto ON- M8V0C1

94A Central Road, Jacanlee, Johannesburg 2194